6. EMPIRICAL EVIDENCE
The CEL (1990) is a theory with roots in Lamarckism and Vitalism. Although it is a general theory, the arguments sometimes refer to the man as being more didactic.
Regardless of the philosophical repercussions, the Conditional Evolution of Life –CEL– contains scientific proposals. Some of them already checked and admitted.
We have presented the CEL proposals in their formulation and conclusions, discussed throughout this book, and listed in the Genetic Variability and Mechanisms of Evolution sections.
Let’s look at the scientific evidence of the most notable:
-
Transmission of genetic information
Lamarck postulated it, and Mendel demonstrated it. It took the scientific community 50 years to recognize and integrate it with Neo-Darwinism. So much delay is because the genetic transmission of all the peculiarities of the new being’s configuration supports 100% of Lamarck’s theory compared to natural selection.
The Mendelian combination causes the distinction between inherited and predestined character. Although there is a transmission of all necessary instructions, they are not always the same.
Another way of saying it would be the famous "Inheritance of acquired characters."
Man evolution is a consequence of the development of genes throughout the life of individuals –CEL.
Modern Darwinism has also adapted the full transmission by bringing the natural selection to the cellular level.
However, character changes are not by accident or by purely random methods but also by intended enhancements. The intentionality comes from very complex and logical modifications in a single generation.
Recently, academia tries to maintain Darwinism by mixing the epigenetics concept –offspring development conditioned to the environment and transmission through RNA instead of DNA. As far as we know, Darwin did not mention where mutations should be.
On the other hand, this point implies a mechanism to move the normal cells’ genetic information to the reproductive cells.
Evidence:
- ♦ 1992-11-26 Regulatory instructions
- ♦ 2002-04-24 The EDI Study (2002)
- ♦ 2002-01-23 Olfactory preferences
- ♦ 2005-(video) Homo Futurus, la evolución del ser humano. Canal Odisea. -Anne Dambricourt- YouTube (es)
- ♦ 2008-05-10 The inheritance of the acquired characters
- ♦ 2017-08-25 Trans generational epigenetic inheritance *
- ♦ 2017-04-22 Environmental ‘memories’ passed on *
- And many others
Ensure the viability of the offspring
There are two main methods: producing abundant offspring with small variations and sexual differentiation in complex organisms.
The first one uses random processes and has justified Darwinism despite no proof these processes were unintentional. Equivalently, the modern lottery is haphazard and, of course, designed by man.
In its early days, genetic modifications were random mutations with Darwin, and there was evidence. Later, they are random only at specific points; later on, their name is not mutations, but Darwinism is still the prevailing theory of evolution.
-
Sexual differentiation
It is the second method of ensuring said viability. It does not eliminate random processes, but it is difficult to justify their complexity with them. Above all, it verifies specific aspects of a logical or non-random nature typical of vital impulse systems.
The most prominent are:
One sex transmits a viable copy of the genome
Not just one copy, but many times partial copies of the genome doubled, tripled, or more –CEL.
Evidence:
- ♦ 1993-01-15 Recover deleted traits
- ♦ 2001-02-28 Hitchhikers on the chromosomes
- ♦ 2002-04-25 Genome of rice
- ♦ 2005-03-30 Backup copy
- ♦ 2012-09-06 Junk DNA comes to light
It is a fact known for scientific advancement. At the beginning of this century and before, there was talk of junk DNA. In other words, the doctrine calmly insulted Nature.
Of course, reducing Life to random processes is not bad either, and more as an example of scientific knowledge. See reflections on why Darwin’s Theory prevailed.
Besides, the same-sex specializes in the technology of materials and the offspring’s initial development –CEL.
Evidence:
- ♦ 2002-01-23 Women have a better sense of smell. And surely ear and taste
- ♦ 2002-01-23 Olfactory preferences
-
The other sex specializes in improving transmitted genetic information –CEL.
Evidence:
- ♦ 1993-05-12 Men suffer more genetic mutations
- ♦ 2001-02-19 The evolutionary progress
- ♦ 2002-01-23 Olfactory preferences
- ♦ 2002-04-24 The EDI Study (2002)
- ♦ 2003-06-21 Human Y chromosome
- ♦ 2003-06-21 Chromosome Y
- ♦ 2010-01-13 chimpanzee and human Y chromosomes
- ♦ 2016-08-01 Male-lineage transmission of an acquired metabolic phenotype **
- ♦ 2016-12-22 Fears and memories inherited via sperm **
The filter function of genetic modifications –CEL
In humans, and probably in all superior animals, the sons between a man and his sister are feasible. Still, they are likely to have serious problems, probably caused by the lack of contrast of the genetic variations with a real external source. It also gives us an idea of the vast number of variations taking in only one generation, despite general assumptions.
-
Method of Logical Verification of Information –LoVeInf
It is not a logical filter to search for errors but rather to use the two sources of information with logical selectors such as addition or intersection to achieve different results.
The LoVeInf method’ scientific evidence comes not only from the initial EDI Study but also from the multiple experiments not carried out but possible such as Darwinout and Menssalina, and others on cognitive abilities’ variables to the extent that there are indicators. The Global Cognitive Theory proposes models according to CEL forecasts in its field.
Evidence:
- ♦ 2002-04-24 The EDI Study 2002)
- ♦ 2016-11-03 One brain, many genomes **
- ♦ 2017-02-23 Some neurons choose mom’s gene, and others select dad’s *
Definition of the significance of genes –CEL
The greater precision of the function of dominant and recessive genes causes a new definition. Depending on the LoVeInf method, the same gene can behave as prevalent for one role and as recessive.
A characteristic may also require both parents to transmit it.
Evidence:
- ♦ 2002-04-24 The EDI Study
-
Hereditary nature of intelligence (r² up to 0.99 in groups of 10 people) and significance of the chromosome with the least intellectual potential for this case –CEL
Evidence:
- ♦ 2002-04-24 The EDI Study
Intelligence effect on sexual selection –CEL
The demonstration occurs by incorporating an additional hypothesis on sexual selection in The EDI Study’s statistical model in September 2002.
Globus Model
Internal evolution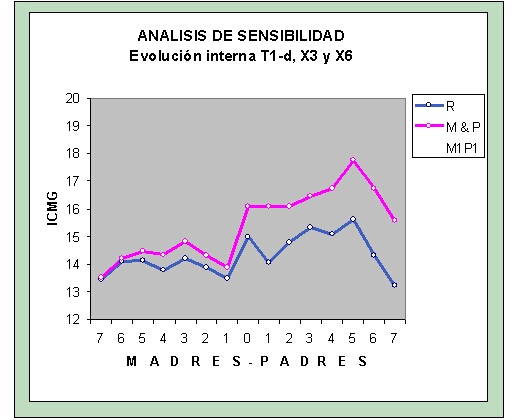
The figure shows the impressive model goodness-of-fit with real data and calculated data according to the CEL and the additional hypothesis.
Evidence:
- ♦ 2002-09-24 EDI study - Additional hypothesis sexual selection.
Sensitivity analysis
Globus Model with sexual selection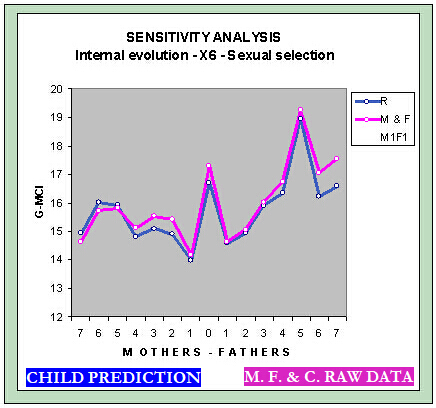
- ♦ 2002-09-24 EDI study - Additional hypothesis sexual selection.
Congruence with relevant historical aspects of human civilizations:
Evidence:
- ♦ 2014-01-30 What we have of Neanderthal
- ♦ Section 8.c) Evolution and economic development
The biological basis of language ability
Some theories support the vision of CEL developed in the Global Cognitive Theory regarding language evolution. After decades, experiments show particular DNA sequences affecting it.
Language evolves, and not all languages have the same number of words or the same precision when it comes to exposing complex concepts such as legal regulations.
Evidence:
- ♦ 2001-10-04 The language gene
Evolution in the form of a foam and not a tree –CEL
The foam form is equivalent to the missing link’s possible non-existence because evolutionary leaps typically occur by combining two or more different genetic lineages.
It has taken the scientific community 30 years to recognize that Neanderthal, Cro-Magnon, and other subspecies interbred.
Evidence:
- ♦ 2001-02-19 Horizontal transference
- ♦ 2010-12-16 Hybrid love and X chromosome
- ♦ 2014-01-30 What we have of Neanderthal
- ♦ 2017-02-03 Stone Age and modern populations in East Asia **
- ♦ 2017-02-20 Interspecies love-ins (en) *
- ♦ 2018-03-06 Two lineages merged, not converged *
- ♦ 2018-08-23 Daughter Neanderthal and Denisovan **
Simulation with genetic algorithms of CEL
The free billiard game Esnuka (1992) allows intuitive assimilation of new concepts.
Sometimes, computerized genetic algorithms for evolution confirm Darwin’s Theory. In this case, how could it be otherwise? They ensure the CEL because they have its genetic algorithms.
The only difference is that it appears to be no Darwinian algorithms successfully simulating the evolution of intelligence.
Evidence:
- ♦ 1992-11-16 Billiards Esnuka
-
Other non-Darwinian mechanisms
Advances in biology and genetics provide knowledge that hardly fits with Natural Selection’s theory or its many updates. They do not even square with the Synthetic Theory of Evolution even though its name seems to integrate whatever is necessary to maintain the Darwinian philosophy.
The CEL does not expressly mention the following mechanisms, but they are in the third point of its formulation: “The systems, methods or processes of evolution are multiple, configured for each case based on certain conditions (and not only environmental but also logical)."
Evidence:
- ♦ 1993-01-15 Rapid adaptation - The Spanish mountain cats
- ♦ 1993-04-26 Wilm tumor
- ♦ 2001-02-19 Horizontal transference
- ♦ 2001-03-14 Eukaryote
- ♦ 2001-03-19 The simplest way of life
- Indeed many others have been discovered.
Scientific innovations can have consequences in philosophy; in other words, aspects considered philosophical could become scientific or vice versa, but the academic community needs time for its assimilation and much more for its transmission to society in general.
A shift in generally accepted notions is a significant barrier, as Thomas Kuhn’s sociology of science de Thomas Kuhn states.
At the risk of making redundant repetitions, it took almost 50 years to recognize and incorporate Mendel’s laws into the dominant theory, the mixture of Neanderthal and Cro-Magnon, about 30 years. We are not sure about Galileo’s heliocentrism because it was a long time ago.
The delays mentioned above are due to sociological and emotional aspects that slow down scientific discussion.
It is possible that with Social Darwinism or the book "The Bell Curve" by Herrnstein and Murray, something similar happens when proposing evolutionary conceptions that do not please certain idealistic ideologies. An idealism that does not prevent accusing scientific positions of barbarities or thinking that the Cro-Magnon had nothing better to do than exterminate the Neanderthal.
Anyway, it is okay. It is not the first time, nor will it be the last for these attitudes to occur.
Like life itself!
