STATISTICAL GRAPH
The title of each graph of the statistical study indicates the parents' variables (R or M & F) to which the correlations relate. Each point of the colored lines represents the correlations with the observational C variables of the children.
Likewise, the variables of unknown order, formed by the different groups of 1 to 10 values from the 70 IQ values of each parent and children variables, appear on the left-hand side of the graph. The criteria order of the groups of 1 to 10 values located on the right-hand side is the variable mentioned at the bottom of the graph.
Indeed, there is an almost instantaneous perception of the exactitude of the particular specification of the statistical study; each graph shows sixty coefficients of determination (r²) highlighting the global and underlying relations of the involved data set.
See the methodology of the statistical abstract for more details
STATISTICAL STUDY COMMENTS
1. General statistical significance
The considerable increase of the correlation for the estimation of homogenous groups is not due to the reduction of 68 to 5 or 4 degrees of freedom, since the estimation with non-homogenous groups, without previous rearrangement, has the same degrees of freedom and the correlation even lowers concerning the sample without grouping.
In general, the model of the genetic evolution of intelligence (Mendelian genetics – Conditional intelligence – Global Cognitive Theory) adjusts perfectly, showing an r² superior to 0.9 in several cases. Bearing in mind the tendency to increase the goodness of fit with the size of rearranged groups, we could assume it would be over 0,9 in almost all the cases for grander groups within a more significant sample.
2. Family - Intelligence of identical and non identical twins.
Family relationships are very interesting regarding genetics and intelligence, in fact, the whole EDI study is related to family characteristics.
Some research can be done regarding relations of identical twins, non identical twins, clones and even the effect of intelligence while selecting a partner or sexual selection.
Actually, we know that all C variables correspond to mono-environmental identical twin brothers, whereas W will only be a sibling; for that reason, sometimes they will look alike and others not so much.
It does not seem hard to imagine some interesting studies on these peculiar matters.
For instance, the selection of a partner as an auxiliary mechanism of evolution has been a paradigm since the first developments of the theory of evolution. Darwin himself wrote The Descent of Man and Selection in Relation to Sex (1871) introducing a new factor, sexual selection, through which females or males choose those with the most attractive qualities as their partner.
3. Significant comments on this particular graph
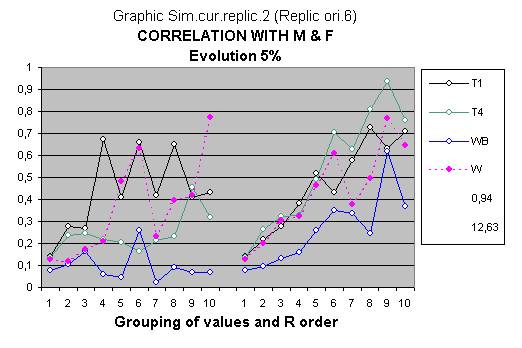
In this graph, the three original dependent variables of the children, analyzed in the model, behave in a very different way to the progenitors' explanatory variables M & F
This graph has been selected because it can be observed that, in the q056, the similarity of the correlation line of the T1 variable with the artificial quotients of W ° intelligence is enormous, and now the same happens but with the T4 variable.
Clearly, it will not always happen and the particular graph has been chosen to call attention to this curious effect, but it has not taken more than ten minutes to find it.
In this case, it appears as if a parameters involve in the computer generation W° variable were straightened up (They were not!), or were more related to the way that functions of the human brain (relating to the different types of intelligence that the T1 and T4 test pick up) are transmitted.
Of course it also could simply be that the entire simulation model’s small randomness could produce this type of variation, which would reaffirm the virtue of the Global model due to the similar behaviour of W (vectors of artificial intelligence quotients created by its computer simulation) with original variables (directly observed IQ vectors)
It does not seem hard to imagine some interesting studies on these peculiar matters.